RG6 vs RG59: A Comprehensive Guide to Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables, often referred to as coax, are a common sight in most households and offices. They are used for a variety of applications, including the transmission of cable television signals, internet data, and more.
Two of the most common types of coaxial cables are RG6 and RG59. While they may appear similar at first glance, there are significant differences between them that can impact their performance in different applications.
This guide will provide a comprehensive comparison of RG6 and RG59 cables, highlighting their construction, performance, and best use cases.

Contents
Understanding the Basics: What are RG6 and RG59?
RG6 and RG59 are types of coaxial cables, distinguished by their construction and performance characteristics. The “RG” in their names stands for “radio guide,” a term that is no longer officially used but has stuck around in common parlance.
Both cables operate on an impedance of 75 Ohms and typically use an F-type connector.
Construction of RG6 and RG59
Conductor
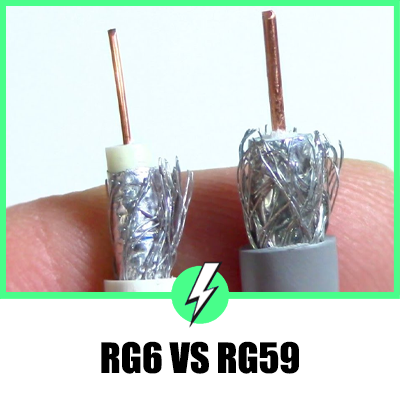
The conductor is the wire in the center of the cable that carries the signal. The conductor in RG6 cables is typically made of copper-clad steel (CCS) and is thicker than that in RG59 cables.
The centre conductor of an RG6 cable is typically 18 AWG (American Wire Gauge) in size, while the centre conductor of an RG59 cable is 20 AWG in size.
Insulation
Insulation is crucial for protecting the cable from environmental damage. Both RG6 and RG59 cables are rated MIL-C-17, the standard grade needed for this purpose.
However, some cables used in harsher environments have a military-grade heavy-duty rating of M17/74, which offers superior protection.
Shielding
Shielding is used to keep ‘noise’ or interference out of your transmission, preserving the quality of your signal. Both RG6 and RG59 cables have a braided metal sheath surrounding a white or clear plastic center that contains a piece of copper.
RG6 cables often have better shielding than RG59 cables, making them a better choice for long-distance transmissions.
Cable Jacket
The cable jacket is the outer layer of the cable, which provides physical protection. RG6 and RG59 can have different jackets, and some are rated for specific installation environments, such as plenum spaces (air-circulating areas above or below the ceiling) or outdoor use.
Performance of RG6 vs RG59
Bandwidth
RG6 cables have a larger conducting wire inside the shielding than RG59, which means they have a higher bandwidth and can transmit more data at a higher rate.
Attenuation
Attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength over distance. RG6 cables generally have lower attenuation than RG59 cables, making them a better choice for long-distance transmissions.
Frequency Range
RG6 cables work best with frequencies at 1 to 5 GHz, making them suitable for high-frequency applications such as broadband internet and satellite TV. On the other hand, RG59 cables are better suited for lower frequency signals, typically 50 MHz or lower.
Uses of RG6 and RG59
RG6 cables are commonly used for broadband internet, CATV, TV antennas, and satellite DSS applications due to their superior performance at high frequencies.
On the other hand, RG59 cables are typically used for analog CCTV, baseband video applications, and other analog video signal transmissions.
Price Difference
Generally, RG6 cables are more expensive than RG59 cables due to their superior performance characteristics.
The Final Word
RG6 and RG59, they may seem similar, but their differences in construction and performance make them suited for different applications. It’s not just about choosing a cable, it’s about choosing the right cable for the job.